07 Apr How to set the standard in Comproved?
The result of an assessment in Comproved is a rank order that classifies students’ works from least good to best. But how do you know who has passed and who has not? In this article, we discuss two ways in which you can set the standard.
The Comproved comparing tool is based on comparative judgement. This is an assessment method in which different assessors are presented with students’ products in pairs and have to indicate each time which of the two, in the light of a given competence, is the better product.
Based on all those choices made by the assessors, the comparing tool estimates a ranking. That ranking is a relative ranking, a ranking where the order is determined relative to each other and not to an external standard. Now, in education, it does matter how good a student’s performance is. We usually measure this by a standard. But how do we get that standard into that relative ranking? We discuss two ways below.
Benchmarks
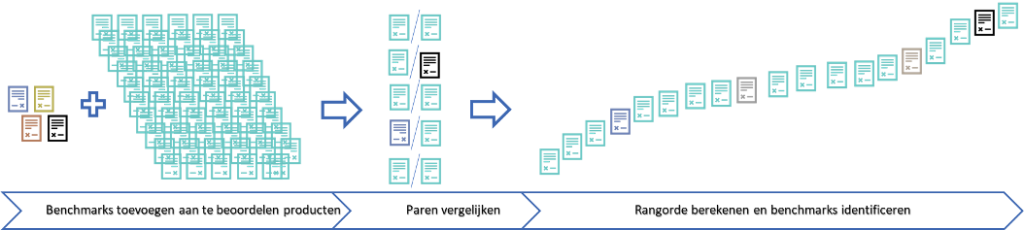
Firstly, you can work with benchmarks. Those benchmarks can be products from previous years. If you give your current students a task similar to a task you gave your students in previous years, you have a lot of products to select benchmarks from. You can select products from all the products from previous years that represent well the scores you want to include. For example, you select a product that represents well what multiple reviewers rate as a 2/10. You can do the same for a 4/10, a 6/10 and an 8/10. You then add these selected products to the products to be rated.
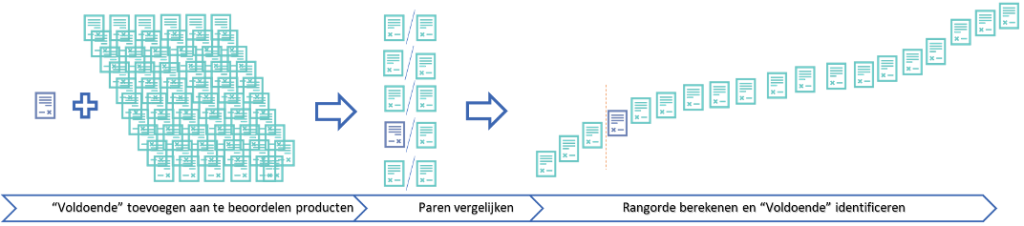
The benchmarks will be sent out in the pairs and thus be assessed and given a place in the ranking. Afterwards, you identify the benchmarks again. This way you have included absolute calibration points in your relative ranking, giving you a good idea of where this year’s students stand. An additional advantage is that you have calibrated the current products with previous years at once.
The “pass”
With a relative ranking it is hard to tell where the pass limit could be. After all, it could be anywhere. If it is at the bottom of the ranking, students have done well. If the pass limit is rather at the top of the ranking, then students still have a lot of margin to improve. And it is certainly not the case that in a relative ranking, the middle of the ranking is the pass limit. So, where to start looking?
At Comproved, we have come up with a way to solve that problem, namely the “pass”. By analogy with benchmarks, you add a product/document to the products to be assessed. In this case, it can simply be a document with just the word “pass” on it. This document will also be sent out in different pairs. Thus, as an assessor, you will often get pairs with students’ products, but you may also get a pair consisting of a student’s product and the “pass” document. That will look like this.
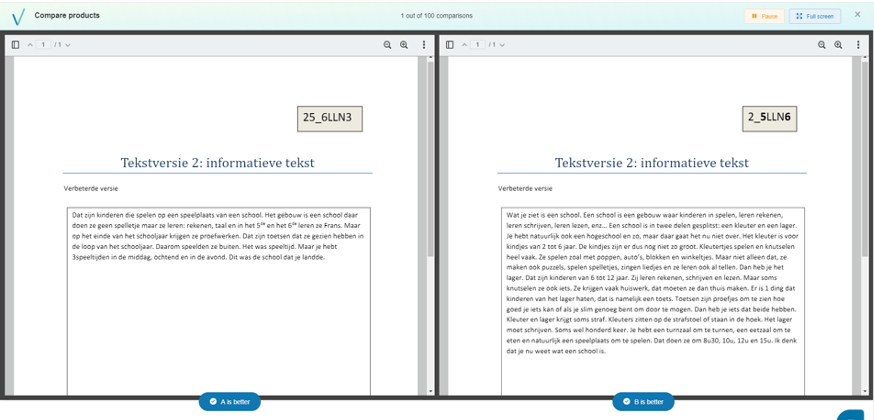
This is an example of a comparison between two student products (in this case, a writing assignment):
And this is what a comparison between a product and the “pass” looks like:
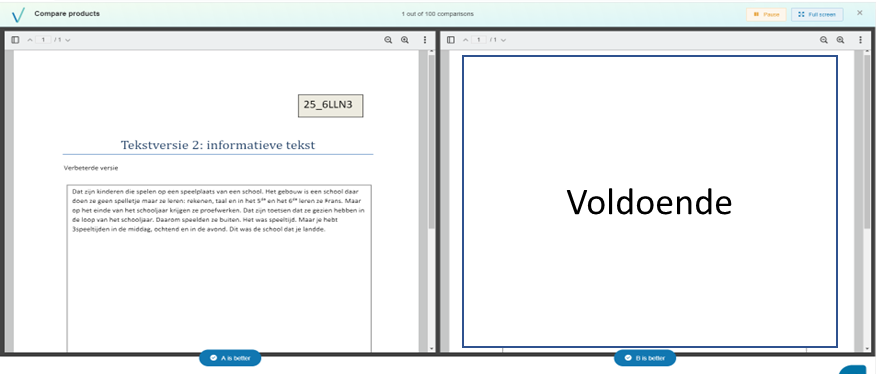
In this case, the question the assessor should ask him- or herself is the following: “Is the product of sufficient quality to pass or not?”. If the assessor judges the product to be a pass, he or she indicates the product as the better of the two. If the assessor judges the product to be a fail, he or she indicates the “pass” as the better product. The “pass” document will therefore be placed somewhere on the final ranking. In this way, you have determined the pass limit in consensus with the co-assessors. To be safe, you can revisit the closest products to estimate whether it is effectively the pass limit. But at least now you know where to start looking.